Ozone Therapy to Fight Stroke, Is It Possible?

Stroke is not unfamiliar if you’re at all concerned about heart health, you probably have a good understanding of cholesterol and blood pressure, and likely know your numbers. But there may be another critical blood-related issue to consider — blood viscosity, or blood thickness. According to a health report from Harvard University, people with thicker, more viscous blood may be at a greater risk for a heart attack or for developing heart disease.
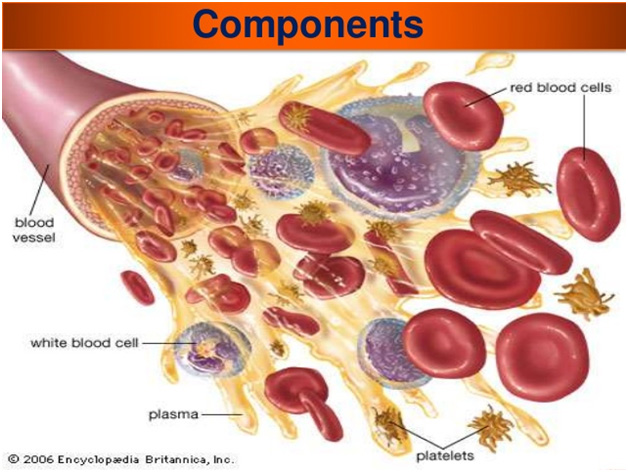
While a person’s blood may look uniform, it’s made of a combination of different cells, proteins, and clotting factors, or substances that aid clotting.
blood veins
The old adage “Blood is thicker than water” makes sense for family ties. But for the heart and circulatory system, though, thinner, more watery blood might be better.
As with many things in the body, blood relies on a balance to maintain a normal consistency. If an imbalance in the proteins and cells responsible for blood and blood clotting develops, your blood can become too thick. This is known as hypercoagulability. An interesting theory proposes that watering down your blood can prevent heart disease.
Some tantalizing threads of evidence suggest that people with thicker (or more viscous) blood have higher chances of developing heart disease or having a heart attack or stroke. Viscosity measures a fluid’s resistance to flow; honey, for example, is more viscous than water.
The more viscous the blood, the harder the heart must work to move it around the body and the more likely it is to form clots inside arteries and veins. Blood that is too thick can lead to blood clots, and blood that is too thin can lead to easy bruising or bleeding. Problems with blood thickness can occur from birth, or develop later in life. Blood thickness may be affected by foods, drugs, and various medical conditions.
Red blood cells have the greatest influence on the blood’s viscosity, since they account for up to half its volume. Your hematocrit is a measure of both the number and the size of red blood cells. In men, a normal hematocrit is between 41% and 53%, meaning red blood cells account for 41%–53% of blood volume; in women, it is between 36% and 46%.
Blood fats such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL, “bad” cholesterol) affect viscosity. The more LDL, the thicker your blood. The same holds true for fibrinogen, a soluble protein that can be transformed into stringy, insoluble fibrin, which forms the semi-solid base of blood clots.
Blood Clots Lead to Stroke
If not prevented or timely detected and treated, blood clots can result in serious complications, such as:
- Deep vein thrombosis – a clot formed in a deep vein in the leg or arm results in pain, swelling and circulation problems around the affected area. If such clot breaks off, it can travel to lungs and cause pulmonary embolism.
- Pulmonary embolism – when a clot in deep vein breaks away and travels back to the heart or lungs, resulting in insufficient blood flow and interfering with gas exchange in the lungs. It may cause chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid breathing, painful breathing, increased heart rate and coughing up blood.
- Stroke – when the blood flow to the brain is blocked either by a blood clot formed on an atherosclerosis plaque within a blood vessel in the brain or by a wandering clot that lodges in an artery leading to the brain. It can cause paralysis, disability, brain damage and even death.
- Heart attack – when a blood clot forms in the coronary artery. It may cause arrhythmias, heart failure or death.
- Kidney failure – when clot blocks one or both of the renal veins. It can cause kidneys unable to remove waste and fluids form the body.
- Pregnancy-related complications – when blood clots as a safeguard against losing too much blood during labor. However, this can cause preeclampsia, stillbirth or miscarriage.
Ozone Therapy For Stroke
In circulatory disease, a clumping of red blood cells hinders blood flow through the small capillaries and decreases oxygen absorption due to reduced surface area. Ozone reduces or eliminates clumping and red cell flexibility is restored, along with oxygen carrying ability. Oxygenation of the tissues increases as the arterial partial pressure increases and viscosity decreases. Ozone also oxidizes the plaque in arteries, allowing the removalof the breakdown products, unclogging the blood vessels.
Read more : Are You Suitable For Ozone Therapy